Usage of Proxy Based Framework in Cloud Computing
April 8, 2022 - Reading time: 6 minutes
With the recent surge in cloud computing, deployment and collaboration in cloud-based systems have become critical for organizations. While the traditional collaborative technologies are functional, they don’t offer flexibility and agility for dynamic collaboration. As the technologies are not very efficient, organizations are bound to keep all their eggs in the same basket, jeopardizing data confidentiality and application security.
A new proxy-based framework proposed for cloud computing has been developed to overcome the issues that the traditional technologies and frameworks face.
What Is Multi-Cloud
Multi-cloud is a practice that involves more than one cloud deployment of the same type. Two types of cloud computing can be employed for deployment and those are categorized into public and prWith the recent surge in cloud computing, deployment and collaboration in cloud-based systems have become critical for organizations. While the traditional collaborative technologies are functional, they don’t offer flexibility and agility for dynamic collaboration. As the technologies are not very efficient, organizations are bound to keep all their eggs in the same basket, jeopardizing data confidentiality and application security. If you design a system with both public and private cloud deployment systems, the setup is called hybrid cloud, which is beyond the scope of this article’s discussion.
A multi-cloud system offers many benefits for an organization. Such as:
No two cloud services are the same. You might find one of those perfect for an aspect of your operation and another for one. Opting for multiple cloud solutions is the best solution for it. But, if you need to collaborate between those two elements, it becomes complicated with a multi-cloud approach.
Despite the development of faster internet connections, poor response time is still an issue for organizations. To diminish the problem, multiple clouds, stationed in different locations help.
Multi-cloud solutions help prevent outages of the main cloud by keeping backups in different locations.
What Is Proxy-Based Framework
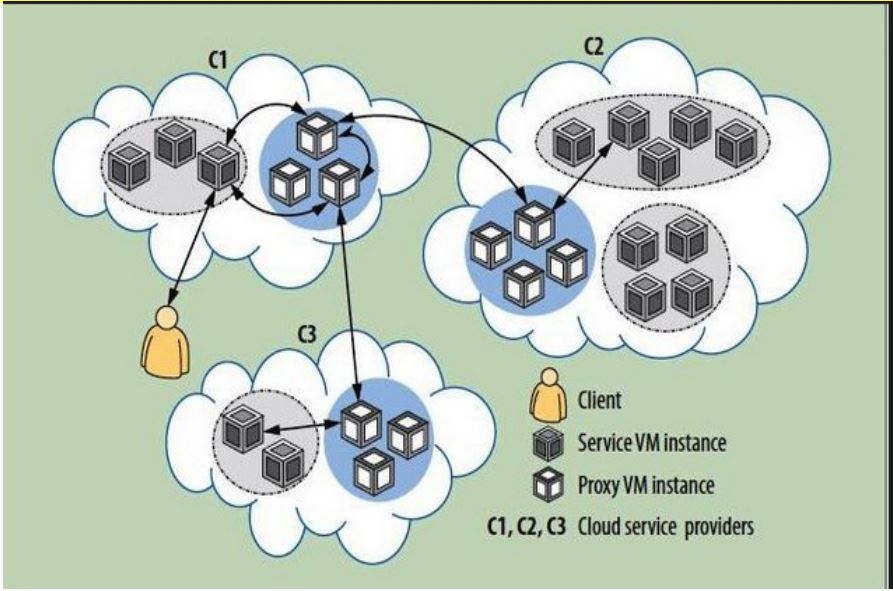
A proxy-based framework or infrastructure for cloud computing is an approach that allows users and applications to use data from multiple clouds simultaneously. As general proxy servers forward your web requests, a proxy-based framework offers dynamic collaboration by forwarding access requests to a multi-cloud system.
Multi-cloud systems lack agility, flexibility, and openness. With the introduction of proxy-based frameworks in the multi-cloud setup, it’s now possible to implement interactions between multiple systems without being bounded by highly controlled, low-level integration techniques.
But, as convenient as the system may sound, it’s unlikely that cloud vendors will accept a centralized system that easily lets users migrate to other services.
The proxy-based framework uses various forms of proxies to ensure the multi-cloud system stays dynamic and secure.
What Types of Proxy-Based Frameworks Can Be Used For Cloud Computing
Proxy as a Service
Just as the name suggests, proxy as a service (PaaS) is a solution that lets other correlated microservices direct their requests through the same server. PaaS ensures that the security and management policies are maintained throughout the microservices. Like residential proxies, PaaS also works as a gateway and forwards the requests originating from different services to their intended destination. But, in the case of residential proxies, the proxy servers forward the requests from a different location.
In a proxy-based framework for cloud computing, multiple cloud services can use the common third-party proxy solution so that they don’t have to implement proxy services on their cloud servers.
Could-Hosted Proxy
A cloud-hosted proxy is already based on clouds and doesn’t employ a hardware setup. Just as with any proxy, cloud proxy servers also forward your request through different servers to communicate further. Your web requests flow through cloud-proxy servers to the websites you want to visit, which then return through the same server to you and fulfill your requirement by keeping you secure from predatory eyes. In proxy-based frameworks for cloud computing, the service provider must host cloud-proxies within their facility to manage and forward the user requests to other cloud systems.
Peer-to-Peer Network
Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks allow multiple systems to share files and resources within themselves without requiring any third-party server or device. In theory, all the computers in the network work both as a client and a server depending on the usage. The sharing policies of a P2P network are defined by the settings of each device taking part in the transmission.
Cloud computing can be implemented through peer-to-peer proxy networks in agreement with cloud providers to offer flexibility and agility.
On-Premise Proxy
On-premises proxies are hosted and managed by organizations that require proxy servers for their projects. On-premises proxies are the most versatile proxy servers that companies can have. As it’s managed by the same organization it’s hosted on, the chances of stolen data, compromised connection, and data outages are minimal.
If your organization is on a multi-cloud system and have the resources to erect on-premises proxy servers, in collaboration with the cloud providers, they can deploy proxy-based frameworks for cloud computing. For this approach to be successful, all the cloud providers will also have to be on board.
Advantages of Proxy-Based Framework in Cloud Computing
The advantages of a multi-cloud system are well known and discussed before. But implementing a proxy-based framework in cloud computing has advantages beyond that.
Faster Cloud Computation
Multiple cloud vendors implement different security and data policies for their products. A proxy solution will require them to abide by the same policies throughout their cloud servers. What it changes is that if you need to collaborate between projects on different servers, you won’t need to abide by different rules and can execute jobs faster.
Fragmentation
Application logic can be faulty. Presently, the data and application need to be housed on the same server because the infrastructure is not fast enough to collaborate them. With the introduction of proxy-based frameworks, data and application logic can be separated from each other, and sensitive data can be protected from leakage due to application logic faults.
Data Confidentiality
As no one cloud provider will not be having all data of the same project, data confidentiality is maintained. This works in two ways. First, the application logic, any cloud provider won’t have access to the full application logic if it’s distributed between different cloud servers in micro fragments. Second, the cloud providers won’t have access to the whole calculated results. Thus, data confidentiality interests are protected.
The Bottom Line
The proxy-based framework approach promoted dynamic collaboration between multiple cloud systems. Proxy servers act as an intermediary to facilitate operations that need to share data. This framework has the potential to overcome multiple difficulties that multi-cloud systems face while trying to collaborate between applications. The developers are trying to develop a viable proxy-based framework depending on use cases and security requirements. Although the development is still in its infancy, the potential of this technology is unrivaled.
by Dani Martin
